An Aromatic Compounds and Their Reactions Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet
Aromatic compounds are a class of organic compounds that contain one or more aromatic rings. An aromatic ring is a stable, cyclic arrangement of atoms with alternating single and double bonds, known as pi bonds. These compounds exhibit a unique property called aromaticity, which is characterized by the presence of delocalized pi electrons within the ring structure. Aromatic compounds have a wide range of applications in fields such as pharmaceuticals, polymers, agrochemicals, and dyes.
Aromatic compounds include a wide range of organic compounds that contain one or more aromatic rings, such as:
Benzene
Toluene
Naphthalene
Anthracene
Phenol
Aniline
Pyridine
Furan
Thiophene
Indole
Here’s a brief cheat sheet on Aromatic Compounds and their reactions in Organic Chemistry:
- Aromaticity: Aromatic compounds are cyclic compounds with alternating double bonds (pi bonds) which follow the Hückel’s rule: 4n+2 pi electrons (where n is any integer).
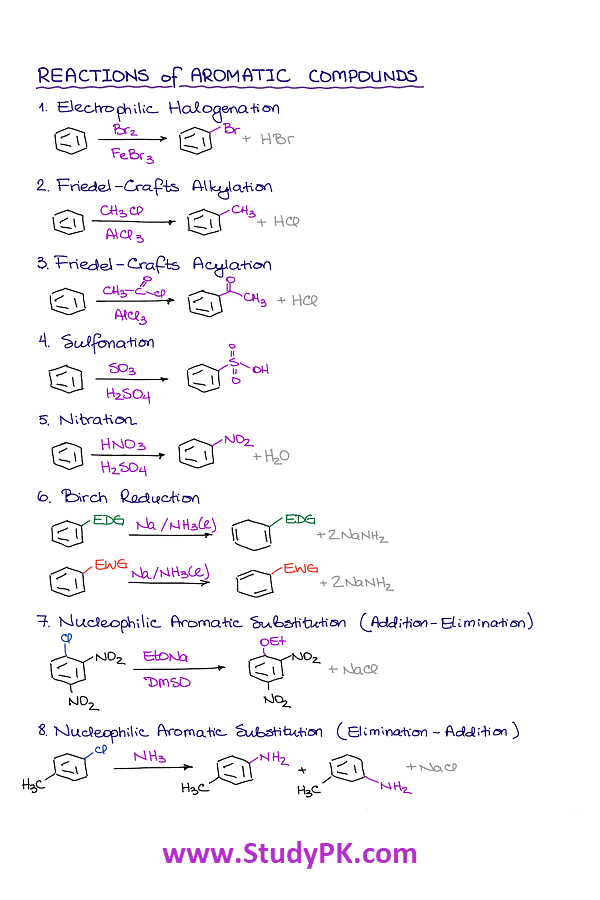
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Electrophilic substitution reactions of arenes involve the replacement of a hydrogen atom on the ring by an electrophile, such as NO2+, Br2 or SO3.
- Friedel-Crafts Alkylation: This is a reaction between an alkyl halide and an aromatic compound in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst such as AlCl3 or FeCl3.
- Friedel-Crafts Acylation: This is a reaction between an acyl halide and an aromatic compound in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst such as AlCl3 or FeCl3.
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: This is a reaction where a nucleophile (such as OH- or NH2-) substitutes for a leaving group on an aromatic ring.
- Birch Reduction: This is a reduction of an aromatic ring using sodium metal and liquid ammonia. This reduction leads to the formation of a diene.
- Wolff-Kishner Reduction: This is a reduction of a carbonyl group to a methylene group in the presence of hydrazine and a strong base.
- Clemmensen Reduction: This is a reduction of a carbonyl group to a methylene group in the presence of amalgamated zinc and hydrochloric acid.
- Sandmeyer Reaction: This is a reaction where an aryl diazonium salt is converted into different functional groups such as halogens, nitriles or hydroxyl groups.
- Reimer-Tiemann Reaction: This is a reaction where phenol is treated with chloroform and NaOH to produce salicylaldehyde.
Leave a Reply